GMC Automatic Transmission Problems
GMC vehicles are known for their reliability and performance, but like any other vehicle, they can experience transmission issues. In this informative video, we’ll explore the most common GMC transmission problems, their symptoms, and how to fix them. From slipping gears to delayed shifts, our expert guide will help you identify and address these issues before they escalate. Don’t let transmission troubles slow you down.
GMC trucks, vans, and SUVs manufactured by General Motors (GM) include Yukon, Terrain, Acadia, Canyon, Sierra, and Savana models. This article will tackle some of the most common problems and issues with GMC vehicles. Here, we document some GMC transmission issues, common causes, and tips on troubleshooting GMC transmission problems yourself.
Here are Common GMC Automatic Transmission Problems
Symptoms
- GMC won’t move when placed in the drive
- The shifter won’t shift out of the Park.
- Can not move shifter back to Park.
- Check engine light stays on.
- The vehicle is stuck in fail-safe mode. Also known as the limp mode.
- The vehicle will not change gears.
- The vehicle won’t move in any gear.
- Transmission slips.
- Harsh shifting.
Common Causes
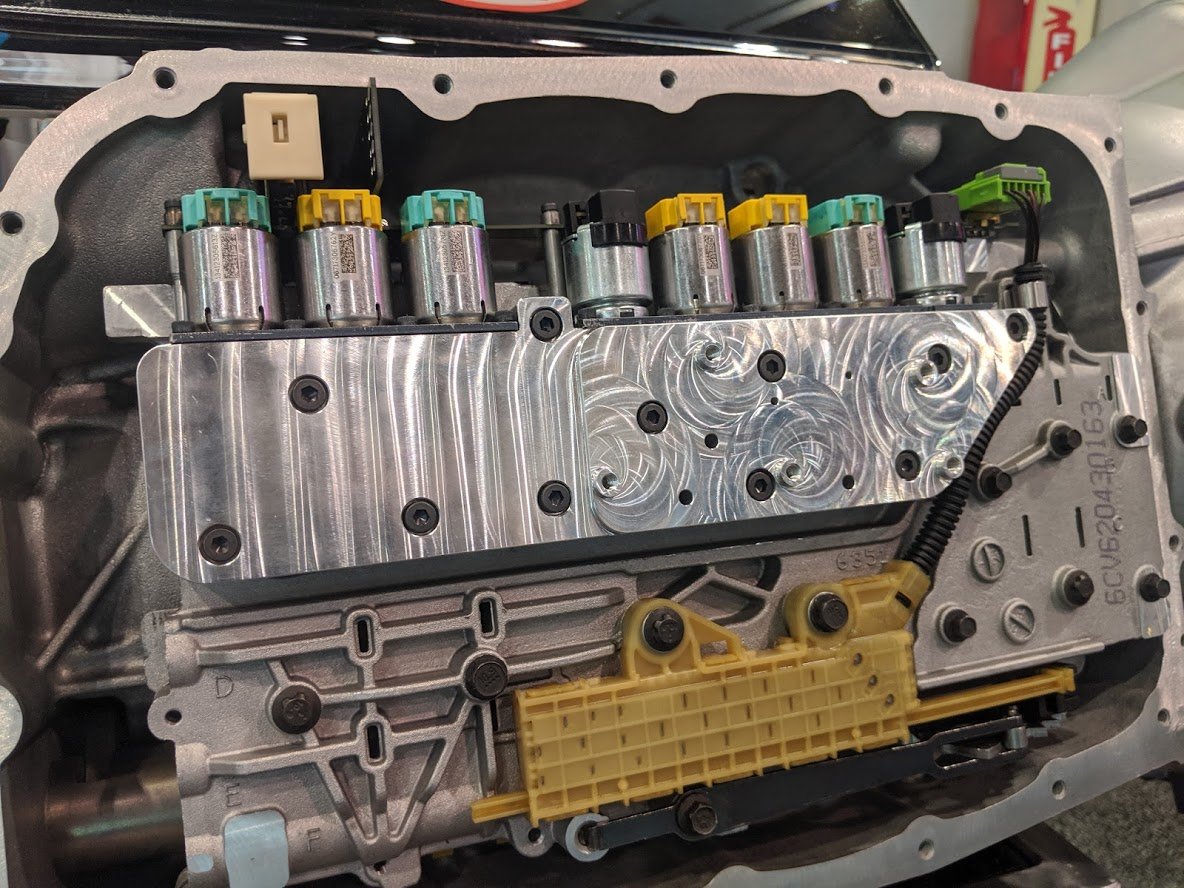
- Low transmission fluid level – A low transmission fluid level is one of the most common issues that prevent a GMC vehicle from shifting when placed in the Drive (D) or Reverse (R).
- Shifter link – The shifter link connects to the transmission valve body. A misaligned shifter link or rod can prevent the transmission from moving when placed in Drive. That’s because even though you have selected Drive or Reverse, the transmission is not in the same gear.
- Brake light switch – If you can not move the shifter out of the Park or back into the park position, the problem can be a faulty brake light switch. Other possible cues include a bad ignition interlock or a faulty shifter.
- Valve Body – A faulty valve body can cause several problems in a GMC vehicle. You may notice harsh shifting, delayed shifts, car shifts only at high RPMs, or not shifting.
- Vehicle Speed Sensor – The transmission vehicle speed sensor does not only cause erratic shifting; it often leads to the transmission getting stuck in one gear (limp mode) and triggers the check engine light.
- Overheating – Overheating of transmission fluid is another common problem that can lead to harsh shifting issues and premature failure of a GMC transmission. Overheating is a concern on GMC trucks frequently used for towing or hauling heavy loads.
Common GMC Transmission Problems
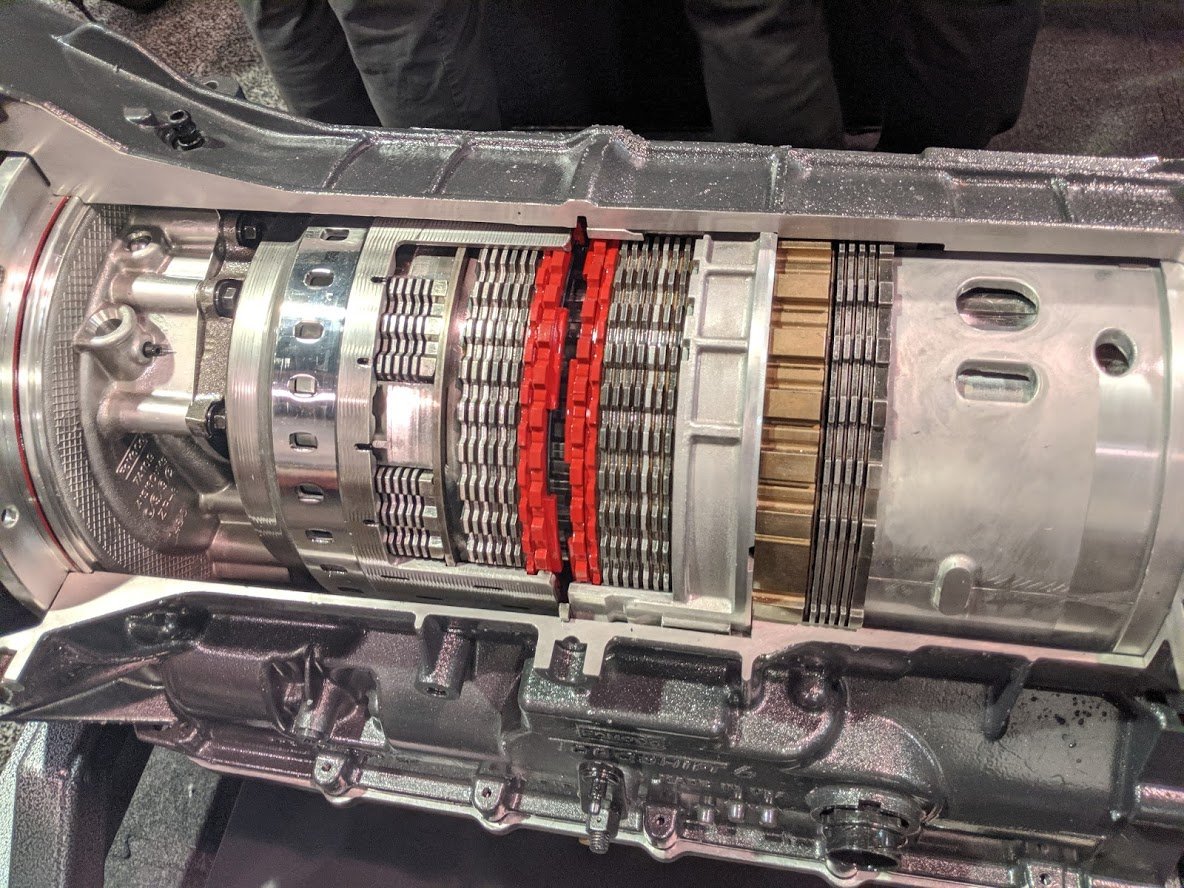
Delayed or Incorrect Shifting
GMC vehicles that use a 4-speed automatic 4L60E or 4L65E transmission can develop a problem with gear shifts. This issue will manifest as improper gear changes that take too long. In some cases, the transmission will not downshift during accelerations. These symptoms can be constant or intermittent and may trigger the check engine light and a transmission-related code such as P0700.
Possible causes and solutions:
- Faulty throttle position sensor, which sends incorrect data to the TCU. This is likely to trigger a check engine light. A fault code will also be stored in the Engine Control Module (ECU) memory. The operation of the throttle position sensor can be monitored and verified using most diagnostic tools.
- A worn Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) regulator valve will cause harsh shifting from 1st to 2nd gear. This will trigger a check engine light and may also trigger fault code P1870 code. The regulator valve is inside the body, and numerous rebuild kits have upgraded components. See GMC Transmission Rebuilt Kits.
- Clogged or faulty shift solenoids, resulting in electrical glitches or jammings. If the fault is electrical, it may trigger a check engine light. Mechanical issues and clogged solenoids will rarely result in a check engine light.
Missing higher gears or transmission stuck in 1st gear.
GMC vehicles that use a 4-speed automatic 4L60E or 4L65E transmission can have intermittent or constant problems when switching to higher gears. There are two usual scenarios. In one, the vehicle will refuse to shift from 2nd to 3rd gear.
In the other one, only the 1st gear will be available, and the vehicle will refuse to engage any 2nd-4th gear and reverse.
Possible causes and solutions:
- Worn clutch pack for 3rd and 4th gear, resulting in the inability to engage 3rd gear. The wear happens over time because of a leak within the piston that engages the clutch. The solution is to replace both the engagement piston and the clutch pack.
- Broken drive shell collar or worn collar splines limit the transmission to 1st gear only. Other drive gears and reverse are no longer available. In most cases, this happens suddenly and stays that way. Replacing the drive shell is the only solution.
No reverse available
GMC vehicles with a 4-speed automatic 4L60E or 4L65E transmission can have intermittent or constant problems selecting reverse. This will manifest as an inability to engage the reverse gear while there are no issues with the engagement of other gears. There will be no other symptoms.
Possible causes and solutions:
- The worn or faulty servo engages the reverse gear. When it starts leaking, it will not be able to create the oil pressure needed for gear engagement. Replacing it is easy, but the oil pan and valve body must be removed.
Incorrect gear shifts, gear slipping, or overheating.
Newer GMC trucks with 6-speed 6L80 transmission can suffer intermittent or constant transmission issues. Symptoms include harsh or delayed shifting, inability to engage certain gears, and slipping when shifting gears. These problems can even lead to transmission overheating in some cases.
Possible causes and solutions:
- A worn pressure regulator system ensures the correct hydraulic pressure needed for proper transmission operation. When parts inside this system wear out, the pressure drops and causes various shifting issues. The solution is to rebuild or replace the pressure regulator system.
Shaking and shuddering during gear changes
GMC vehicles with 8-speed 8L90 and 8L45 transmissions have a widespread problem known as the ‘Chevy shudder.’ The symptoms during gear shifts typically include shaking, juddering, and harsh shifting. In severe conditions, it may be followed by a noticeable clunk. Issues are usually present during any gear change, although more noticeable in 1st and 2nd gear.
Possible causes and solutions:
- Incorrect transmission fluid type is a well-known and documented problem with all GM vehicles that use this 8-speed transmission. A Technical Service Bulletin (TSB 18-NA-355) describes how replacing factory-installed transmission fluid with Mobil 1 Synthetic LV ATF HP fluid solves the issue.
- The glazed torque converter results from prolonged usage with the shudder problem present. This will cause similar symptoms even after the transmission fluid has been flushed, and replacing the torque converter is the only solution.
Improbable Transmission Temperature
GMC vehicles with 8-speed 8L90 and 8L45 transmissions can develop intermittent problems regarding the transmission temperature. Symptoms that drivers can experience include improbable temperature readings, overheating, slipping, and harsh shifting. These issues trigger a check engine light, so a fault code will be stored in DTC memory.
Possible causes and solutions:
- Faulty transmission fluid temperature sensors send incorrect and implausible data. The TCU will recognize this and trigger a P0711 code. Besides the sensor, both the wiring and connector might be broken.
- Low transmission fluid level or dirty filter, which can cause overheating. High fluid temperatures will cause other issues with transmission operations.
Troubleshooting GMC Transmission Problems
Most GMC transmission problems, such as harsh shifting, delayed shifting, no gear, stuck in gear, and no reverse or drive, are often caused by low transmission fluid levels. Check the transmission fluid if your GMC vehicle with automatic transmission is not shifting properly. See the instructions below on how to check the transmission fluid level on a GMC.
If the transmission fluid level is correct, use a transmission scanner to read fault codes via the OBD-II port. See the instructions below.

The YOUCANIC Full System Scanner can read and clear fault codes through every vehicle’s control module.
- Park the vehicle and turn off the ignition. Set parking brakes.
- Locate the diagnostic port under the dashboard, driver’s side.
- Plug in your OBD-II scanner, then turn on the ignition without starting the engine.
- The scanner will turn on. Allow it to communicate with the vehicle. Select GM, then your particular model.
- Select Control Units, then Transmission.
- Select Read Fault Codes from the menu.
These instructions work on all 2000 and newer GMC trucks, including Yukon, Terrain, Acadia, Canyon, Sierra, Savana, etc. The scanner will display a fault code, for example:
- P0700 – This is a generic code, meaning there is a malfunction with the transmission. The check engine light will be on, and the transmission may be in failsafe mode.
- P0729 – is defined as the Incorrect Gear Ratio.
- P0741 – There is a significant difference between the torque converter and the transmission input shaft.
These are general codes. You will get more detailed descriptions using a transmission scanner that can read GMC-specific codes. Research each code and remember that many possible problems could cause the same code.
We hope you find the GMC Automatic Transmission Problems guide helpful. Check these troubleshooting and repair guides for more help on your GMC.









Hi Mike, If you read the codes from the transmission control unit (may be called power train on that model), you will have a better idea of what is wrong with the transmission and why it is stuck in first gear.
2013 GMC Terrain. Installed new engine. Transmission worked fine with no problems. Now engine run as it should but transmission only has 1st gear. Hooked to analyzer and will not read just spins. Not reading. Any Ideas. All I can find is don’t buy a terrain. It’s a little late on that.
I have a 2012 2500 GMC with a allison trany When the oil is minus 10C or colder it won’t move till the oil temp gets to minus 8C I had the oil and filter changed and flushed But the problem is still there. The shop said the oil was a little milky indicating water contamination. I belive that happaened when I backed into deeper water to unload my boat 18 months ago When the oil warms up it works 100%