Fixing Mercedes EBR, ABS, ESP Inoperative Issues: Comprehensive Guide
It is crucial to understand each warning of your vehicle when your Mercedes flashes EBR, ABS, or ESP inoperative messages and how to address the problem to ensure your vehicle’s performance and safety. This comprehensive guide will delve into the common causes behind these messages and offer expert advice on troubleshooting and resolving the problems. Our step-by-step instructions will guide you in diagnosing these problems with your Mercedes and guarantee that your luxury automobile is continually operating at its peak condition. The vehicle may seem to brake and function normally, but the anti-lock braking and stability functions are disabled.
What do Brake, EBR, ABS, and ESP messages mean?

One reason this message may cause confusion is that it mentions several systems that practically get disabled simultaneously. An anti-lock Braking System, or ABS for short, is a safety device that prevents the wheels from locking up when braking hard. This shortens the stopping distance to the minimum and allows the driver to steer the vehicle during this maneuver.
ESP, which stands for Electronic Stability Program, will stop the vehicle from sliding and keep it on an intended trajectory. It does that by detecting understeer or oversteer and applying the brake to one or more wheels to stabilize the vehicle. Unlike ABS, this happens even when the driver does not press the brake.
Certain Mercedes-Benz cars come with EBR or EBD, which stands for Electronic Brake Regulation/Electronic Brake Force Distribution, to enhance braking performance further and improve stability. If an EBR error appears on your instrument cluster, your Mercedes-Benz is required with EBR, but the system is temporarily disabled.
This system adjusts the brake system balance depending on different factors, such as road conditions and load distribution inside the vehicle. It does this by proportioning the brake force between the front and rear wheels to match their grip levels. This makes braking more stable when things like turning cause weight shifts, which might offset the brake balance.
What causes the ‘EBR, ABS, and ESP inoperative’ message?
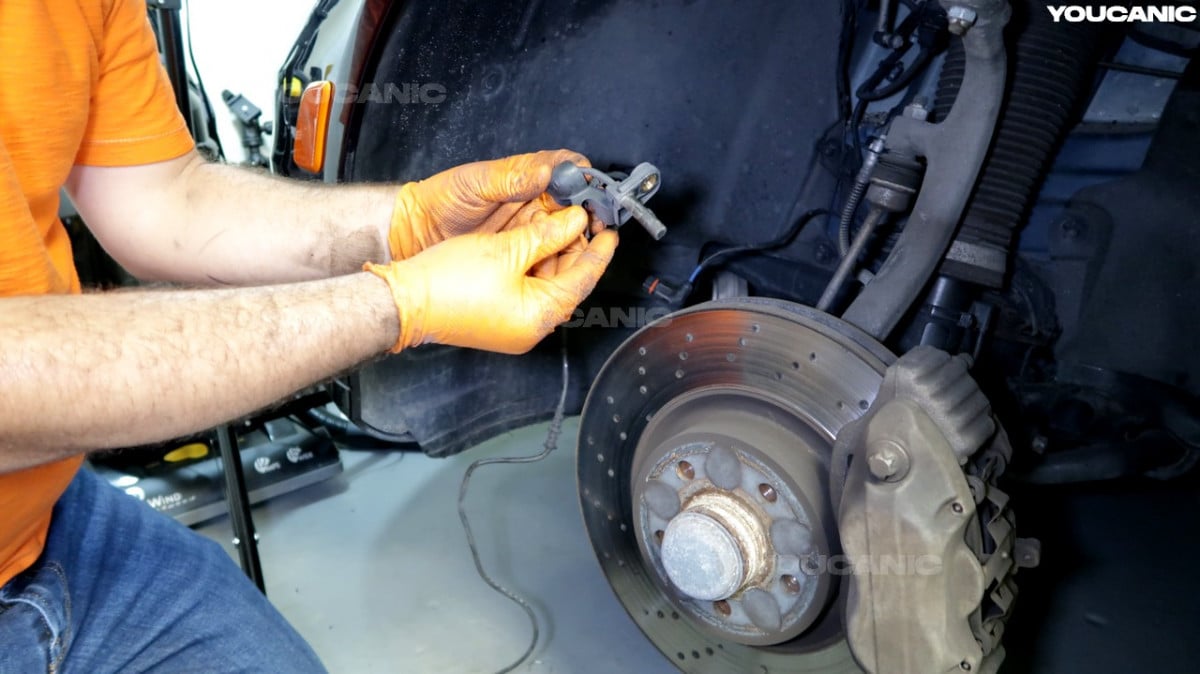

The most common problems that trigger EBR, ABS, and ESP inoperative error messages to come up are:
- Damaged ABS wheel speed sensor
- A weak vehicle 12-volt battery
- Bad alternate or voltage regulator
- The steering angle sensor needs calibration or replacement
Brake assistance systems, including EBR, ABS, and ESP, are elaborate systems with many sensitive components and sensors.
A malfunctioning sensor could bring multiple systems down, affecting vehicle braking performance and stability. Just like with other devices, there are many potential causes, and these are only a few common ones:
- Voltage drops caused by a worn battery or faulty alternator may affect the operation of both ABS and ESP. This is because all the sensors and components require a steady voltage, and even the slightest irregularity might offset their function. These systems will also go offline if the owner replaces the battery without connecting the vehicle to a trickle charger.
- All cars have a brake light switch that, as its name indicates, illuminates the brake lights when slowing down. ABS and ESP systems use this signal to recognize when the driver presses the brake pedal. With time, internal components of this simple sensor may wear out, making the signals coming from it implausible. The software inside the ABS module will recognize these faulty signals and shut down the system as a preventive measure.
- Being exposed to dirt and corrosion, wheel speed sensors and their wiring are other components that are likely to fail. They will give inaccurate readings that will confuse the ABS module. Tracking down the faulty sensor requires a suitable diagnostic tool, as there are four total. To locate a defective wheel speed sensor, you can use the YOUCANIC diagnostic tool.
- Although reliable and rarely fails in general, the ABS module itself can affect the operation of these brake systems. Among possible causes, things like worn hydraulic valves or faulty solenoids that control their movement are the most likely. The new module is expensive, so sourcing a remanufacturer may be more feasible.
- If one of the Wheel Speed Sensors has no readings, you can identify which sensor is faulty by using the YOUCANIC diagnostic tool. Go to the brake system’s live data and search the wheel speed sensor data reading. Test drive your vehicle to confirm if all the wheel speed sensor readings are identical. If one has a different reading, that might be the issue.
How do you reset the ABS and ESP in a Mercedes-Benz?
A simple method to fix brake, EBR, ABS, and ESP warnings involves restarting the vehicle and turning the steering wheel to the left and right with the engine on. Repeating this procedure several times may reset ABS and ESP systems, clearing the warning message from the display.
If the main battery is the issue, replacing the battery can solve the issue. To determine the cause of these warning lights, you must read the codes to precisely determine the problem.
The YOUCANIC Full System Scanner is a perfect example of an OBD-II scanner for troubleshooting your EBR, ABS, and ESP. This powerful device can read and clear fault codes from all systems, perform bidirectional tests, perform maintenance and repair resets, and perform many more professional-grade functions that can help you determine the cause of the problem.

How do these safety systems work?
The working principle behind EBR, ABS, and ESP systems is similar, as they share most hardware. There is a speed sensor at each wheel knuckle, which measures how fast they are spinning. Next, a steering wheel angle sensor gives information about where the driver points to the vehicle. Similarly, a rotation sensor will reveal if the car is sliding or spinning out of its path.
In the end, a load sensor measures the weight of the passengers and luggage against the rear axle. Combined, this data gives perspective on the vehicle’s speed and behavior on the road.
The ABS module, sometimes called the Hydraulic Electronic Control Unit (HECU), is the central component operating all three systems. This device is an integral part of the brake system and its hydraulic circuitry, into which it taps. If the wheel tracks between brakes during braking or other maneuvers, the ABS module will take suitable action to regain it. Locking up will continuously reduce and re-apply braking force until the wheels grip up again. If the vehicle begins to slide or spin, the ESP will apply the brake to one or two wheels.
Conclusion

In conclusion, taking the time to understand and address the EBR, ABS, and ESP inoperative warnings on your Mercedes is an essential aspect of responsible vehicle ownership. By following the expert guidance and recommendations in this comprehensive guide and reading the fault codes from all the systems using the YOUCANIC scanner, you can accurately diagnose and resolve these issues, ensuring a smooth and safe driving experience.
If you’re ever uncertain about any steps in the process, consult your vehicle’s manual or seek professional assistance. Your Mercedes-Benz deserves only the best care possible, and eliminating these issues quickly proves your commitment to maintaining its performance and safety.
As explained here, ESR, ABS, and ESP are abbreviations for safety systems that improve vehicle stability during harsh braking. These warning lights are often triggered due to a faulty ABS wheel speed sensor, but you must read the codes to determine precisely the issue.
References
- Power Steering Malfunction, Brake (EBR, ABS, ESP Inoperative) Errors On C350 2009 – mbworld.org
- EBR, ABS, and ESP Inoperative – benzworld.org
- Im getting the EBR ABS ESP inoperative message. – Justanswer.com
- Ebr, abs, esp warning – MBClub.co.uk







this was very good help for me because i didnt know. now i understand whats going on.