Chevrolet Read & Clear Fault Codes
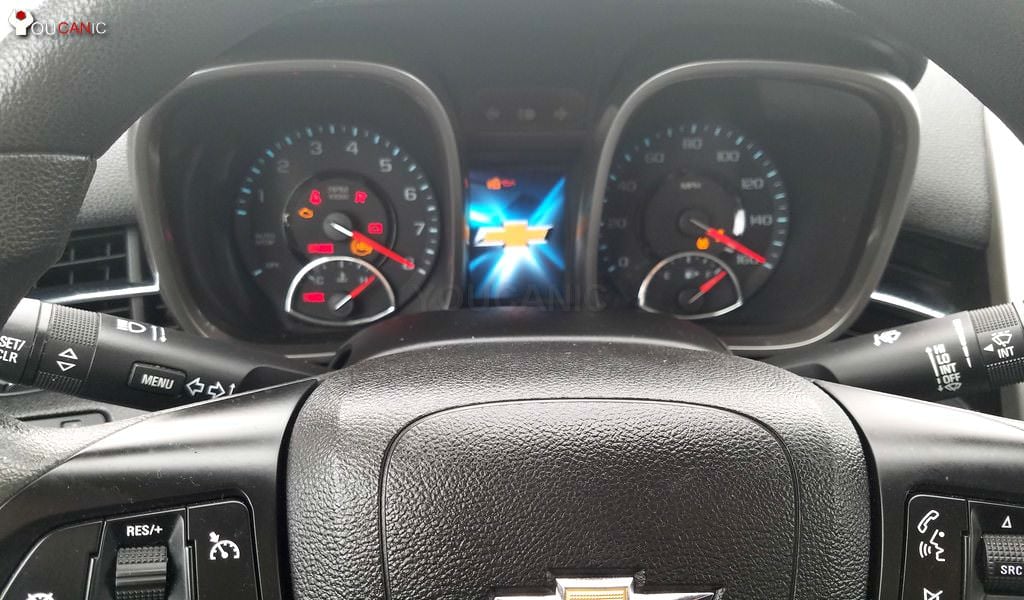
Do your Chevrolet Check Engine Light (CEL) or other warning lights like ABS, Airbag, and TPMS stay on? Learn how to fix it by following the procedures below.
What you will need

- YOUCANIC Full System Scanner – This powerful scanner can read and clear codes from all the systems present in your Chevrolet.
Procedure
- Park the Chevrolet on a level surface and set the parking brakes.

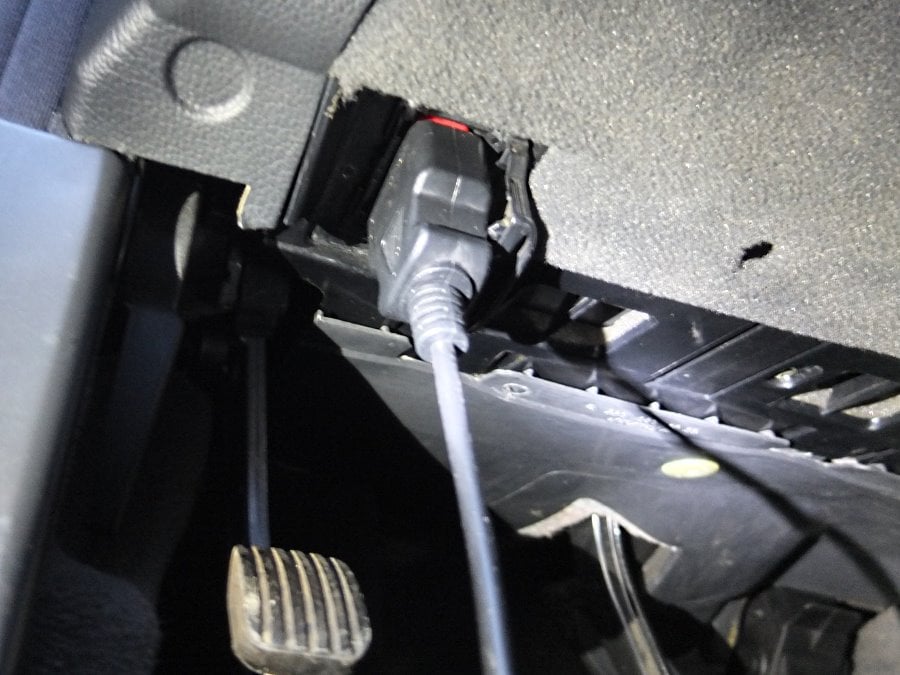
- Open the driver’s door and locate the OBD-2 port.
- Plug your scanner into the OBD2 port.

- Turn on the ignition by turning the key to position II. If your Chevrolet has a START/STOP button feature, press the button without pressing the brake pedal.

- Allow your scanner to turn on. Follow the prompts on your scanner to read fault codes.
- Access the Diagnostic Menu: On the YOUCANIC scanner’s display, navigate to the “Diagnostic” or “Scan” menu. This menu allows you to access various diagnostic functions for your Chevrolet.

- Select ‘Chevrolet’ as the Vehicle Make: This ensures the scanner effectively communicates with the Chevrolet On-Board Diagnostic system and effectively scans the fault codes.

- Select option for model selection: The scanner has various options for model selection. You can choose SmartVIN to detect your vehicle automatically. However, you choose Manual Selection if SmartVIN does not work as intended.
- Select the Specific Model and Chassis: After selecting the vehicle make, scroll through the available models and select the correct one for your Chevrolet. Choose the corresponding chassis or body type to properly sync the scanner to your vehicle. Check our article here to learn more about the VIN of your Chevrolet.

- Select Control Units: Once you have selected the model and chassis, the scanner will let you choose between “Quick scan” or “Control Modules”. Control Modules display a list of control units or modules in your vehicle. Examples include the engine control module (ECM), transmission control module (TCM), and ABS control module. Choose the specific module you want to diagnose. Otherwise, you can also choose the “Quick Scan” to check everything.

- Erase Codes: After the problem has been repaired, return to the scanner’s menu and select the option to “Erase Codes” or “Clear Codes.” This action removes the stored fault codes from the control unit’s memory, indicating that the problem has been resolved. Please note that you may or may not erase a code when the issue is not fixed.

Common Chevy Fault Codes
- P0300 – Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected:
- Possible Causes: Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, or a failing Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor.
- P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1):
- Possible Causes: Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, clogged fuel injectors, or a malfunctioning fuel pump.
- P0174 – System Too Lean (Bank 2):
- Possible Causes: Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, clogged fuel injectors, or a malfunctioning fuel pump.
- P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1):
- Possible Causes: Faulty catalytic converter, oxygen sensor, or exhaust leaks.
- P0700 – Transmission Control System Malfunction:
- Possible Causes: Faulty transmission control module, wiring issues, or internal transmission problems.
- P0750 – Shift Solenoid A Malfunction:
- Possible Causes: Faulty shift solenoid, wiring problems, or low transmission fluid.
- P0785 – Shift/Timing Solenoid Malfunction:
- Possible Causes: Faulty solenoid, wiring issues, or low transmission fluid.
- C1214 – Brake Control Relay Contact Circuit Open:
- Possible Causes: Faulty relay, wiring problems, or ABS module issues.
- C0267 – Pump Motor Circuit Open/Shorted:
- Possible Causes: Faulty motor, wiring issues, or ABS module problems.
- B0012 – Driver Frontal Deployment Loop Stage 1:
- Possible Causes: Faulty airbag, wiring problems, or a defective airbag SRS module.
- B0022 – Driver Side Deployment Loop Open:
- Possible Causes: Faulty airbag, wiring issues, or a defective airbag module.
- B0081 – Passenger Presence System (PPS) Sensor Circuit Malfunction:
- Possible Causes: Faulty sensor, wiring issues, or issues with the airbag module.
- P0442 – Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak):
- Possible Causes: Loose or damaged gas cap, vacuum hose leaks, or problems with the EVAP system components.
- P0128 – Coolant Thermostat (Coolant Temperature Below Thermostat Regulating Temperature):
- Possible Causes: Faulty thermostat, low coolant level, or a malfunctioning engine coolant temperature sensor.
- P0404 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Open Position Performance:
- Possible Causes: Stuck EGR valve, clogged EGR passages, or faulty EGR position sensor.
- P0507 – Idle Air Control System RPM Higher Than Expected:
- Possible Causes: Dirty or malfunctioning idle air control valve, vacuum leaks, or a faulty throttle body.
- P0601 – Internal Control Module Memory Checksum Error:
- Possible Causes: Faulty PCM (Powertrain Control Module), software issues, or wiring problems.
- P1133 – Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) Insufficient Switching (Bank 1 Sensor 1):
- Possible Causes: Faulty oxygen sensor, exhaust leaks, or problems with the fuel system.
- P1134 – Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) Transition Time Ratio (Bank 1 Sensor 1):
- Possible Causes: Faulty oxygen sensor, wiring issues, or exhaust system problems.
- P1516 – Throttle Actuator Control (TAC) Module Throttle Actuator Position Performance:
- Possible Causes: Faulty throttle body, throttle position sensor issues, or wiring problems.
- P1682 – Ignition 1 Switch Circuit 2:
- Possible Causes: Faulty ignition switch, wiring issues, or problems with the starter circuit.
- U1000 – Class 2 Communication Malfunction:
- Possible Causes: Wiring problems, faulty control modules, or network communication issues.
- U1016 – Loss of Class 2 Communication with VCM:
- Possible Causes: Faulty Vehicle Control Module (VCM), wiring problems, or network communication issues.
- U1041 – Loss of Electronic Brake Control Module (EBCM) Communication:
- Possible Causes: Faulty EBCM, wiring issues, or communication problems in the brake system.
Please note that these codes and causes are for general reference.
Diagnose Chevrolet ABS Anti-lock Brake System
An ABS light cannot be diagnosed with a generic OBD2 scanner. You will need an ABS diagnostic scanner like the YOUCANIC Full System Scanner.
Diagnose Chevrolet SRS Airbag Light
Like the ABS light, your Chevrolet SRS Airbag lights cannot be diagnosed with a basic OBD2 scanner. You will need a multi-system scanner.
Knowing which scanner to use to read Chevrolet fault codes can be challenging. Basic OBD2 scanners can only retrieve fault codes from your Chevrolet Engine Control Unit ECU. Those are faults that trigger the Check Engine warning light.
You will need an advanced scanner to diagnose systems such as ABS and Airbag/SRS warning lights. The procedure for reading Chevrolet fault codes is similar, regardless of which scanner you use.
A Powerful scanner that can help you easily read and clear codes on your Chevy is the YOUCANIC Full System Scanner. This powerful scanner can perform many tasks compared to a generic OBD-II reader. It can also perform bi-directional tests, maintenance, reset functions, etc.
We hope you find this “Chevrolet Read & Clear Fault Codes” guide helpful. Check these troubleshooting and repair guides for more help on your Chevrolet vehicle.