Honda Check Engine Light Stays On
A Honda vehicle’s check engine light (CEL) is a warning indicator that something is wrong with the engine or emissions system. It can indicate various problems, including issues with the fuel system, catalytic converter, oxygen sensor, spark plugs, and more. It is important to address any issues the CEL indicates to avoid further damage and keep the vehicle running safely and efficiently. A certified mechanic can use diagnostic tools to read the vehicle’s diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), determine the specific issue causing the CEL, and make the necessary repairs.
A steady check engine light means there is a present issue. Continue driving with caution if you don’t notice any performance issue. Do not drive if the car overheats or the oil light is on. If the check engine light is flashing or blinking, it means a serious engine problem, such as a misfire.
The engine will shake, and you will notice a poor throttle response. It is not recommended to drive your Honda if the check engine light is flashing. Driving a car when the check engine light is flashing will damage your catalytic converter and cause the engine to overheat.
Symptoms
In addition to the check engine light (CEL) coming on, you may also notice the following.
- Engine Shaking
- Rough Idle
- Emission System Problem message on the dashboard
- Honda check engine light flashing.
- The engine idles too high.
- Poor acceleration
- Difficulty going uphill
- The car won’t start
- Honda dies when placed in gear.
The Honda check engine light may occasionally come on, but no other symptoms are present. This would be the case with a loose gas cap.
How to Diagnose Honda Check Engine Light

As a mechanic, the first step in identifying the cause of a Honda check engine light (CEL) would be to use a diagnostic tool to read the vehicle’s diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). These codes can provide information about the issue causing the CEL to turn on. The DTCs will give a specific code, such as P0171, which indicates that the engine control module (ECM) has detected a problem with the fuel system, specifically a lean condition in the fuel mixture. Another code could be P0420, indicating that the catalytic converter is not working efficiently.
Once the DTCs have been read, the mechanic would thoroughly inspect the vehicle’s systems to identify the cause of the problem. This may include inspecting the engine, emissions system, sensors, and wiring.
For example, if a DTC indicates a problem with an oxygen sensor, the mechanic would inspect the sensor for damage or malfunction and check for any other issues affecting the sensor’s performance, such as a vacuum leak or a clogged fuel injector.
If your Honda check engine light is on, the first thing that you, your mechanic, or your dealer should do is scan the engine codes using an OBD-II scanner. Honda-specific scanners will provide more information and scan more systems than a generic scanner.
The YOUCANIC Full System Scanner can read and clear the code, giving you a good idea of what is causing the check engine light to stay on.
- Locate the OBD-II port under the dashboard, driver’s side.

- Connect the OBD-II scanner.
- Turn on the ignition.
- Allow your scanner to turn on and communicate with the Engine Control Unit (ECU). Select Read Codes from the main menu. Next, select Current Codes. Your first code will show up, such as P0300 – Cylinder Misfire. Scroll up and down to see all stored codes.
Write down the code and search for the fault code online. If you don’t have an OBD2 scanner, visit a Honda dealer or an auto mechanic. Auto parts stores such as Advance Auto Parts and Autozone will scan the codes for you free of charge.
Common Problems
Let’s look at some common problems that trigger the Honda check engine light to stay on.
Oxygen sensor
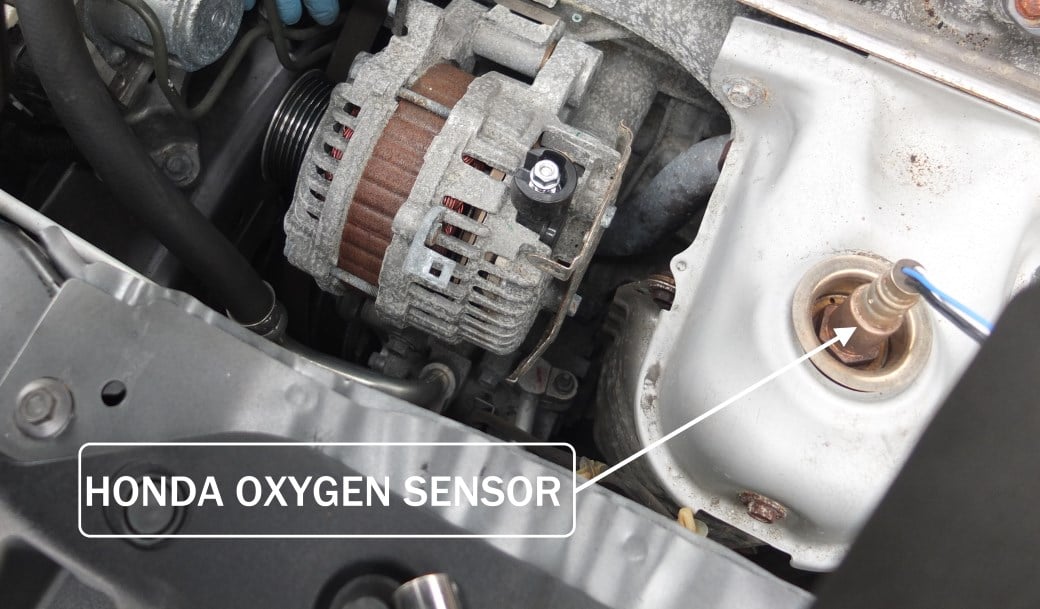
O2 sensor performing below efficiency is a widespread problem that will cause your Honda check engine light to come on.
Loose gas cap
A loose or missing gas cap will trigger your Honda check engine light to come on. If you don’t notice any performance issues and check engine light is not flashing, tighten the gas cap and continue driving. If that’s all, your Honda check engine light will reset within two days.
Catalytic Converter
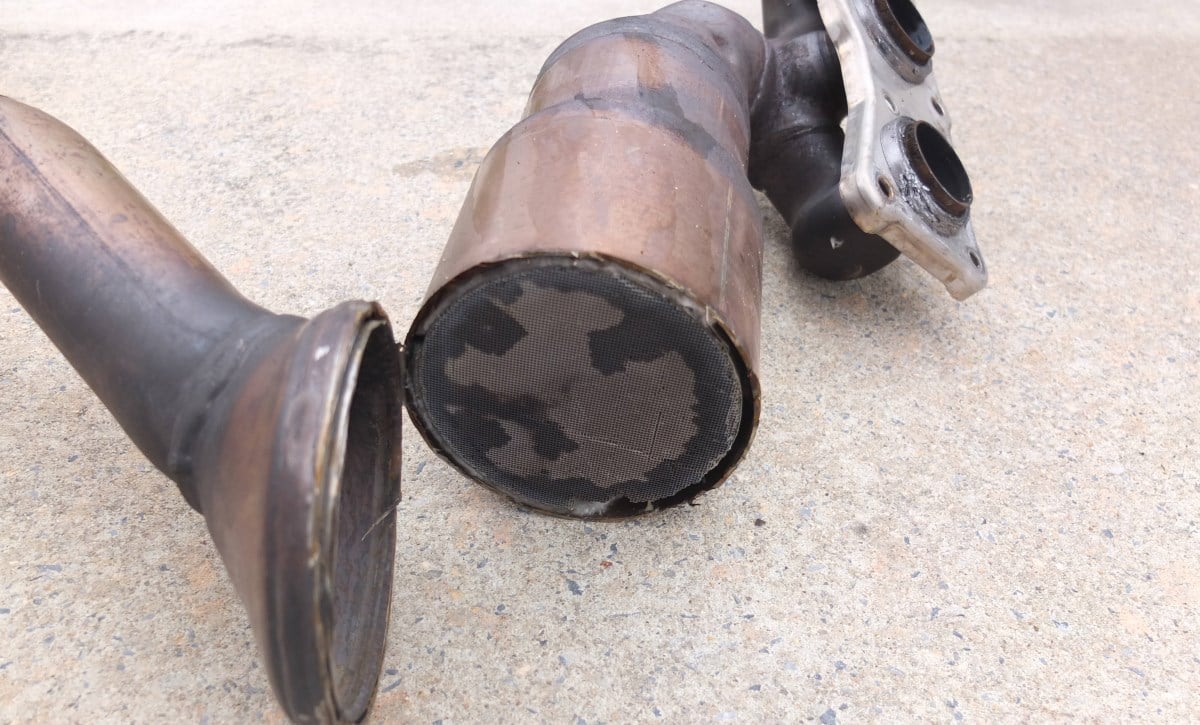

Catalytic converters will trigger the check engine light in your Honda if they are partially clogged. You will notice that the car will shake in addition to the check engine light. The engine runs rough. Also, these symptoms will be worse when accelerating or trying to go uphill.
Spark Plugs

Honda cars last a long time, but spark plugs don’t. Many Honda owners don’t realize that spark plugs must be changed between the 60,000 and 100,000-mile mark.
If spark plugs are not changed at the recommended interval, they will eventually start to wear or, even worse, stop working. Once they fail, they will throw misfire fault codes such as P0300 and cause your engine to shake.
Transmission Problems
Even though Hondas are quite reliable, a few models, such as the Honda Odyssey or Honda Accord, were prone to having transmission problems. Once the transmission fails or slips, you could end up with a check engine light on and a fault code in the P0700-P0799 range, indicating a transmission problem.
Fuel Pump
Honda cars are also known to have issues with the fuel pump. Fuel pump problems don’t always trigger the check engine light. You are more likely to experience no start condition or intermittent starting problems. A bad fuel pump can be tricky to diagnose early because the car may seem to run okay.
A fuel pump starting to fail throws a multiple-cylinder misfire code P0300 before it completely stops working and prevents the car from starting. The Honda check engine light may also be referred to as a soon or malfunction indicator light.
Common Fault Codes
As you read your Honda check engine light with an OBD-II scanner, you will get a fault code that starts with P____. Let’s look at some of the most common Honda engine codes.
P0456 (Evaporative Emissions System – Small leak detected)
- Besides the apparent loose fuel tank cap, this code can be caused by cracks in EVAP hoses or vapor canisters. Purge valves or canister vent valves can be faulty, also.
- The best way to find a fault is to test the whole system with a smoke generator machine. Connect the smoke machine to the EVAP hose on the intake manifold and visually check where the smoke comes out.
P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold)
- If you have this code in your Honda, your downstream O2 sensor’s readings show that the amount of oxygen in the exhaust is incorrect. A faulty catalytic converter can cause this. However, you may also have false readings caused by a bad O2 sensor or damaged sensor wiring.
- Also, exhaust leaks or incorrect ignition timing can cause this code. It is wise to rule out all these possibilities before changing the catalytic converter, as they are costly.
P0141 (Heated oxygen sensor 2, bank 1 heater control circuit malfunction)
- The downstream O2 sensor in your Honda have an integrated heating element to help it reach operating temperatures as soon as possible. It can go bad from usage over the years or be damaged by contaminants, such as water.
- Before changing the sensor, check the fuse in the engine bay. Also, visually inspect the connector and wiring for damage.
P0740 (Transmission Lock-Up Control System Fault)
- Your Honda is equipped with a device that locks up a torque converter. This reduces transmission losses and increases fuel economy. Code P0740 indicates that this system is not working properly. This can be caused by something simple as a low transmission fluid level or dirty transmission fluid.
- It is, however, very common for a torque converter clutch solenoid valve to fail. Another possibility is a damaged valve harness. In some Honda vehicles, the P0740 code may be caused by an overheating torque converter that results from an insufficient flow to the torque converter release circuit.
P0401 ( Exhaust Gas Recirculation Insufficient Flow)
- Honda, like many other cars, has an exhaust gas recirculation system. This has the purpose of reducing emissions. Insufficient flow through this system can be caused by a blocked or cracked EGR tube or a faulty EGR valve.
- Another possibility is a vacuum-related issue, as the EGR valve is vacuum operated. Check the vacuum hoses for damage. Lastly, the EGR differential pressure sensor can fail. To verify this, test the sensor voltage. You should get readings between 0.8 and 1.0 volts.
P1457 ( Evaporative Emissions Control System Leakage EVAP Canister System)
- This code is quite similar to the previously mentioned P0456. The possible causes are similar, ranging from fuel cap issues to EVAP system cracks and leaks.
- However, one thing stands out. EVAP purge control solenoid and two-way bypass valve are the most common causes of this code. Also, the fuel tank pressure sensor can fail.
Honda P0137 (Oxygen Sensor Circuit Low Voltage B1S2)
- If you are getting this code on your Honda Accord, CRV, Civic, or Odyssey, there is a high chance the oxygen sensor has failed. It is best to test the O2 sensor resistance to confirm the oxygen sensor is the culprit.
- Some Honda owners replace the sensor without testing it, considering they often go bad. Other possible causes triggering P0137 include a damaged wire harness to the O2 sensor, engine misfire, and low fuel pressure.
Honda OBD1 Fault Codes.
Code 0 and 11 Electronic Control Module (ECM)
Code1 Heated oxygen sensor A
Code 2 Oxygen content B
Code 3 and 5 Manifold Absolute Pressure
Code 4 Crank position sensor
Code 6 Engine coolant temperature
Code 7 Throttle position sensor
Code 8 Top dead-center sensor
Code 9 No.1 cylinder position sensor
Code 10 Intake air temperature sensor
Code 12 Exhaust recirculation system
Code 13 Barometric pressure sensor
Code 14 Idle air control valve or bad ECM
Code 15 Ignition output signal
Code 16 Fuel Injector
Code 17 Vehicle speed sensor
Code 19 A/T lock-up control solenoid
Code 20 Electric load detector
Code 21 V-TEC control solenoid
Code 22 V-TEC pressure solenoid
Code 23 Knock sensor
Code 30 A/T FI signal A
Code 30 A/T FI signal B
Code 41 Heated oxygen sensor heater
Code 43 Fuel supply system
Code 45 Fuel supply metering
Code 48 Heated oxygen sensor
Code 61 Front heated oxygen sensor
Code 63 Rear heated oxygen sensor
Code 65 Rear heated oxygen sensor heater
Code 67 Catalytic converter system
Code 70 Automatic transaxle
Code 71 Misfire detected cylinder 1
Code 72 Misfire detected cylinder 2
Code 73 Misfire detected cylinder 3
Code 74 Misfire detected cylinder 4
Code 75 Misfire detected cylinder 5
Code 76 Misfire detected cylinder 6
Code 80 Exhaust recirculation system
Code 86 Coolant temperature
Frequently Asked Questions
Are maintenance lights and check engine lights the same thing?
No. Check engine light and maintenance light are not the same thing. Some Hondas, such as Honda Accord, Honda Civic, and Honda CRV, have a maintenance light and the check engine light.
Why are my Honda pilot check engine and vtm-4 light on?
Your Honda is designed to disable a Variable Torque Management 4WD System (VTM-4) if there is a problem with engine operation. When you have a check engine and vtm-4 light on, this will usually indicate a problem with an engine. You need to resolve the engine faults, and the VTM-4 system will usually restart after this.
What do the Honda odyssey check engine and TCS light mean?
TCS in your Honda stands for Traction Control System. If the TCS light is on, the system is not working. Remember that if this light came on accompanied by a ‘check engine light, you probably have either engine or transmission fault. Scan for codes with a scan tool. If you have an engine or transmission problem, take care of that first. This could easily be a cause for a TCS light.
What do Honda Odyssey check engine and vsa?
VSA is short for Vehicle Stability Assist, which helps keep your Honda in the lane. An illuminated VSA light indicates that your VSA is inoperable. A variety of faults can cause this. If the VSA light came on with a ‘check engine light, the root of the problem might be in the engine itself. VSA system is designed to shut off when there is an engine-related problem
What do the Honda check engine light and flashing D mean?
A flashing D usually indicates a problem related to an automatic transmission. Depending on the symptoms, it could be caused by various faults. Something as simple as low transmission fluid will not cause driveability issues. A faulty transmission sensor or solenoid, on the other hand, can make gear shifts hard. In most cases, it will trigger a ‘check engine light. You will need to read the codes to get a better insight.
The Honda check engine light is on, but no codes were found.
When a check engine light illuminates, the code will always be stored in vehicle DTC memory. Some generic OBD2 readers are not able to read manufacturer-specific codes. This means you will only see mandatory powertrain codes (Pxxxx codes).
We hope you find the Honda Check Engine Light Stays On guide helpful. Check these troubleshooting and repair guides for more help on your Honda.










Excellent info – many thanks.
Michelle
Check engine light is on steady. won’t go into overdrive scan only read front bank. No code numbers. Any ideas before i take it back to honda