How to Read and Clear Fault Codes on ISUZU with an OBD-II Scanner
When your Isuzu’s dashboard lights up, and you’re not familiar with it, chances are, a check engine light (CEL) has illuminated, and other error lights such as ABS, SRS, transmission temperature, oil pressure light, battery charging, Differential, Traction control, and many more. Those illuminated symbols are diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), the automotive equivalent of Morse code conveying messages about potential problems with your vehicle. While these codes can be intimidating, understanding them is crucial for maintaining Isuzu’s health and performance. To learn more about Check Engine Light, click our article here.
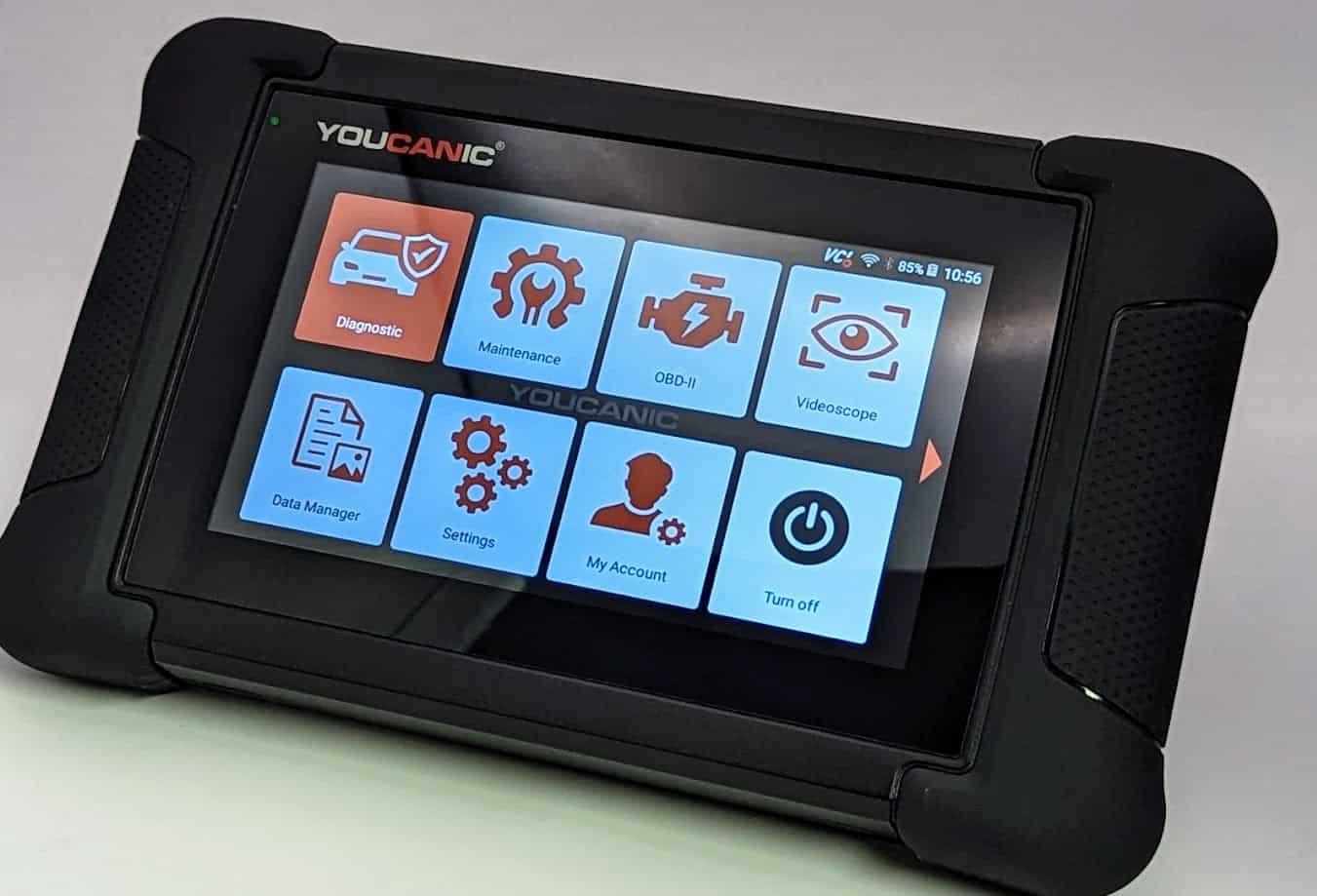
How do I convert these “morse code” or FAULT CODES from computer to human language? You will use an OBD-II Scanner, specifically a Professional-Grade Scanner like our YOUCANIC OBD-II Scanner. It works on all OBD2-compliant vehicles and is designed for professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts.
How to Decipher and Read DTCs or Fault Codes
We’ll Delve into the details for Reading and Erasing DTCs/Fault Codes of Isuzu models like Isuzu Como, Reach, D-MAX, MU-X, Forward, and other newer or older models.
- Gather the necessary tools: Equip yourself with a Professional-Grade OBD-II Scanner compatible with your Isuzu. Click Here for our Professional-Grade YOUCANIC Scanner.

- Access the OBD-II Port: This port is usually found near the steering column under the dashboard. The OBD-II port is the gateway to your car’s diagnostic information. Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine to make a connection with the vehicle’s computer. If your Isuzu has a START/STOP feature, press the button without pressing the brake pedal. Do not start the engine. If you are unsure of the OBD-II port of your vehicle, you can always check the Car Owner’s Manual. Click here if you can’t find your OBD port

- Turn on the ignition, but do not start the engine.

- Access the Diagnostic Menu: On the YOUCANIC scanner’s display, navigate to the “Diagnostic” or “Scan” menu. This menu allows you to access various diagnostic functions for your Isuzu.

- Select ‘Isuzu’ as the Vehicle Make: This ensures the scanner effectively communicates with the Isuzu On-Board Diagnostic system and effectively scans the fault codes.

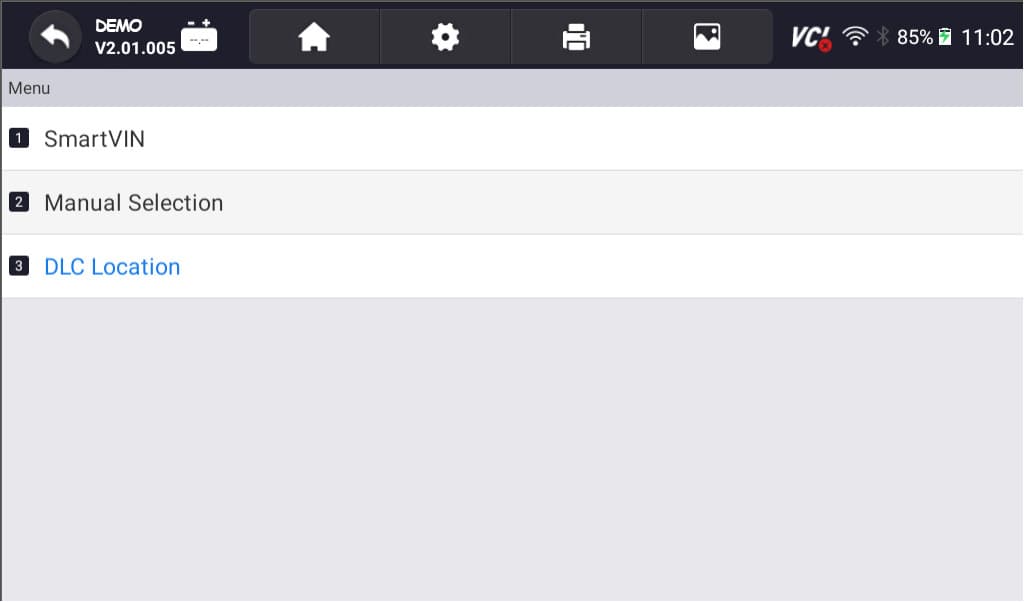
- Select option for model selection: The scanner has various options for model selection. You can choose SmartVIN to detect your vehicle automatically. However, you choose Manual Selection if SmartVIN does not work as intended.

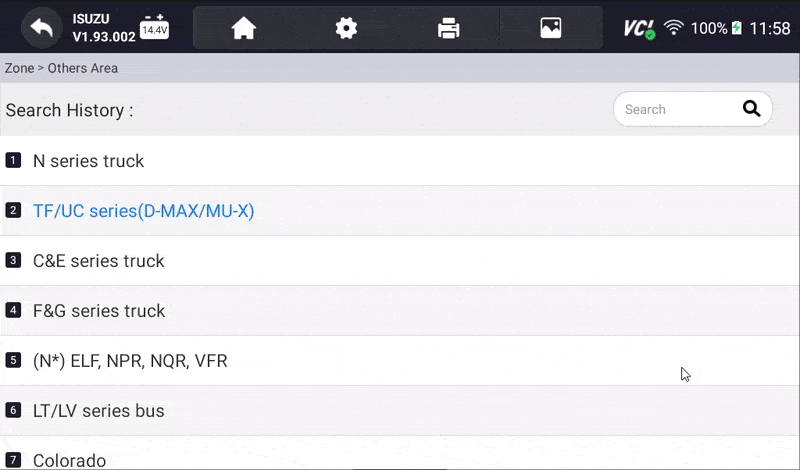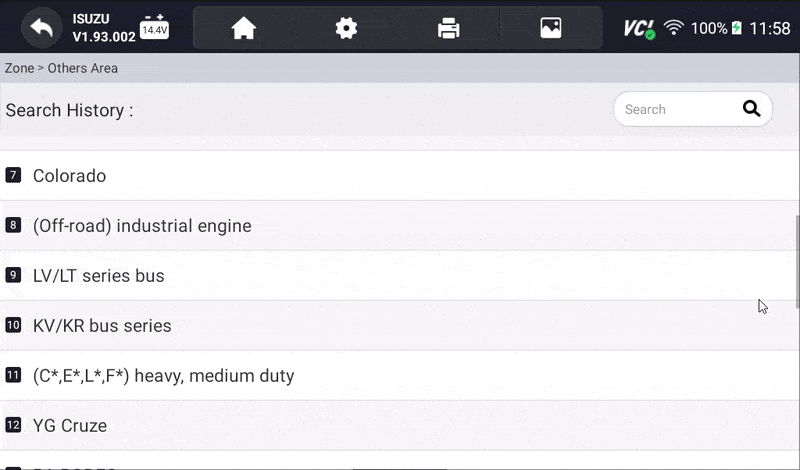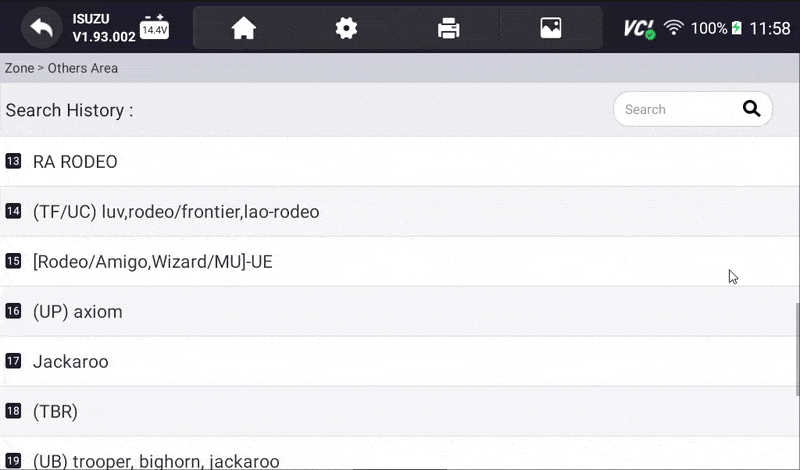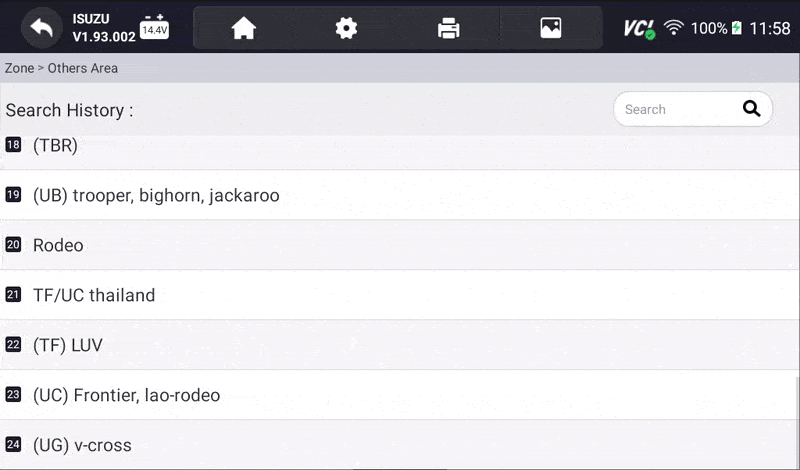
- Select the Specific Model and Chassis: After selecting the vehicle make, scroll through the available models and select the correct one for your Isuzu. Choose the corresponding chassis or body type to properly sync the scanner to your vehicle.

- Select Control Units: Once you have selected the model and chassis, the scanner will let you choose between “Quick scan” or “Control Modules”. Control Modules display a list of control units or modules in your vehicle. Examples include the engine control module (ECM), transmission control module (TCM), and ABS control module. Choose the specific module you want to diagnose. Otherwise, you can also choose the “Quick Scan” to check everything.

- Interpret the Codes: Once the YOUCANIC scanner completes the code retrieval process, the displayed codes will provide information about specific issues detected by the control unit. Take note of these codes for further analysis and diagnosis. Each DTC consists of a letter and four numbers. The letter indicates the system affected, while the numbers describe the issue more specifically. Click here to learn more about Fault codes.

- Erase Codes: After the problem has been repaired, return to the scanner’s menu and select the option to “Erase Codes” or “Clear Codes.” This action removes the stored fault codes from the control unit’s memory, indicating that the problem has been resolved. Please note that you may or may not erase a code when the issue is not fixed.

NOTE: These pictures are just the demo of our YOUCANIC Scanner, it may or may not be the same but the procedure is the same.
Common Fault Codes
Here are 20 common fault codes for Isuzu vehicles, along with their definitions and possible causes:
- P0201 – Injector Circuit/Open – Cylinder 1: Indicates an issue with the injector circuit in cylinder 1, potentially due to a faulty injector or wiring problems.
- P0300 – Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected: This code suggests misfires in multiple cylinders, possibly due to faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or a clogged fuel system.
- P0401 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected: Indicates a problem with the EGR system, possibly due to a clogged EGR valve or faulty EGR sensor.
- P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1): Suggests that the catalytic converter efficiency is below the required threshold, possibly due to a faulty catalytic converter or oxygen sensor.
- P0500 – Vehicle Speed Sensor ‘A’ Malfunction: Indicates a malfunction in the vehicle speed sensor, potentially due to faulty sensor or wiring issues.
- P0700 – Transmission Control System Malfunction: Suggests an issue within the transmission control system, often requiring further diagnostic to pinpoint the exact problem.
- P1239 – Fuel System Lean During Acceleration: This code indicates that the fuel system is running lean during acceleration, possibly due to fuel pump issues or air leaks.
- P0301 – Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected: Specific to misfire in cylinder 1, potentially due to issues like bad spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injector problems.
- P0202 – Injector Circuit/Open – Cylinder 2: Indicates a problem with the injector circuit in cylinder 2, possibly due to a faulty injector or wiring issues.
- P0404 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Circuit Range/Performance: Suggests a problem with the EGR system, possibly due to a faulty EGR valve or clogged passages.
- P0440 – Evaporative Emission Control System Malfunction: Indicates a general malfunction in the EVAP system, potentially due to a faulty purge valve, loose fuel cap, or leaks in the system.
- P0442 – Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak): Suggests a small leak in the EVAP system, potentially due to a loose fuel cap, cracked hoses, or a faulty EVAP canister.
- P0446 – Evaporative Emission Control System Vent Control Circuit Malfunction: Indicates an EVAP system vent control circuit issue, possibly due to a faulty vent valve or wiring problems.
- P0455 – Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Gross Leak): Suggest a significant leak in the EVAP system, possibly due to a loose fuel cap, damaged hoses, or a faulty EVAP canister.
- P0463 – Fuel Level Sensor Circuit High Input: Indicates a high input from the fuel level sensor, possibly due to a faulty sensor or wiring issues.
- P0507 – Idle Control System RPM Higher Than Expected: Suggests the idle RPM is higher than expected, possibly due to vacuum leaks, a dirty throttle body, or a faulty idle air control valve.
- P0562 – System Voltage Low: Indicates that the vehicle’s electrical system voltage is low, possibly due to a failing alternator or poor battery condition.
- P0601 – Internal Control Module Memory Check Sum Error: Suggests an internal error in the control module, requiring replacement or reprogramming of the ECM.
- P1125 – Throttle Position Sensor Intermittent: Indicates intermittent readings from the throttle position sensor, potentially due to a faulty sensor or wiring issues.
- P1290 – Cylinder Head Temp Sensor Low Input: Suggests a low input from the cylinder head temperature sensor, potentially due to a faulty sensor or wiring problems.
As with other vehicle brands, these fault codes in Isuzu vehicles should be considered starting points for a more detailed diagnostic process to accurately identify and address the issues.
How to Decipher DTCs/Fault Codes?
DTCs are standardized codes that follow a specific format, making interpretation easier. This can be seen in the OBD scanner. Each code consists of five characters:
- The first character indicates whether the code is an SAE generic code (applies to all OBDII systems) or is specific to the vehicle manufacturer
- The second character identifies the general type of fault. For instance, ‘0’ indicates a fuel and air metering system issue.
- The third character further narrows down the fault type. It could suggest a circuit malfunction.
- The fourth and fifth characters provide a specific description of the problem.

What do Live data and Freeze data mean?
Live data allows you to monitor real-time sensor readings, providing valuable insights into the car’s operation. On the other hand, Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of vehicle conditions when a fault code is triggered. Analyzing this data provides context and aids in pinpointing the root cause of the issue.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if I ignore DTCs?
Ignoring DTCs can lead to more serious problems and potentially damage your Isuzu’s engine or other components.
Can I clear DTCs myself?
While it’s possible to clear DTCs yourself using a basic scanner, having a professional mechanic diagnose the underlying issue before clearing the codes is recommended.
How often should I scan my Isuzu for DTCs?
Regularly scanning your Isuzu for DTCs, especially if you notice any changes in performance or feel any unusual vibrations, can help identify potential problems early on.
References
- What Is an OBD2 Scanner and How Does It Work?
What Is an OBD2 Scanner and How Does It Work? | The Drive - DTC Fault Codes
DTC Fault Codes – YOUCANIC - What Does the Check Engine Light Look Like, and What Does It Mean?
What Does the Check Engine Light Look Like, and Really Mean? – Consumer Reports - Current / Stored / Active / Past / History Fault Codes Explained
Current / Stored / Active / Past / History Fault Codes Explained – YOUCANIC - A Guide to Understanding DTC Codes
A Guide to Understanding DTC Codes (samsara.com) - DTC Decode – ISUZU
Isuzu Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Definition, Causes and Diagnosis (dtcdecode.com)