Fixing Mitsubishi DTCs: Easy Code Reading & Clearing Guide
Mitsubishi, a name that resonates with precision and innovation in the automotive realm, has carved its niche for over a hundred years with groundbreaking technological feats. This esteemed Japanese brand is celebrated for crafting vehicles seamlessly blending style, performance, and luxury. However, even the most robust Mitsubishi, designed to conquer challenging terrains, isn’t impervious to the occasional dashboard warning lights.
Encountering a lit check engine light (CEL) or other alerts like ABS, SRS, transmission temperature, oil pressure, battery charging, differential, and traction control can be daunting. These lights aren’t just random signals but diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) – your car’s way of communicating specific issues in its intricate systems. While these codes might seem perplexing initially, understanding them is vital to ensure your Mitsubishi continues to perform at its peak. If you’re curious about the Check Engine Light and its implications, delve into our detailed article [here]. Stay tuned as we embark on an engaging journey to demystify these codes and guide you on how to read and clear them effectively.
DIY vs. Professional Car Repairs: What’s Best for You?

While some basic DTC Scanners are available for DIY enthusiasts, professional-grade scanners offer a more comprehensive and accurate diagnosis. All Mitsubishi models from 2001 now include an OBD-II port for easier diagnosis and repair. It can also include Live and Freeze data and access deeper levels of vehicle data, providing more detailed information. YOUCANIC Pro Scanner offers a professional-grade scanner that DIY enthusiasts can use because of its easy-to-use interface and real-time data display. You can also add video scope to see mechanical issues. It is important to ask for assistance, especially when the problem persists or is complex.
How to Read and Clear DTCs or Fault Codes
We’ll dig into the details for reading and erasing DTCs/fault codes of Mitsubishi models like Mitsubishi Pajero, Outlander, Eclipse Cross, Mirage, and other newer or older models.
- Gather the necessary tools: Equip yourself with a Professional-Grade OBD-II Scanner compatible with your Mitsubishi. Click Here for our Professional-Grade YOUCANIC Scanner.

- Access the OBD-II Port: This port is usually found under the dashboard, near the steering column; the OBD-II port is the gateway to your car’s diagnostic information. Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine to make a connection with the vehicle’s computer. If your Mitsubishi has a START/STOP feature, press the button without pressing the brake pedal. Do not start the engine. If you are unsure of the OBD-II port of your vehicle, you can always check the Car Owner’s Manual. Click here if you can’t find your OBD port

- Access the Diagnostic Menu: On the YOUCANIC scanner’s display, navigate to the “Diagnostic” or “Scan” menu. This menu allows you to access various diagnostic functions for your Mitsubishi.

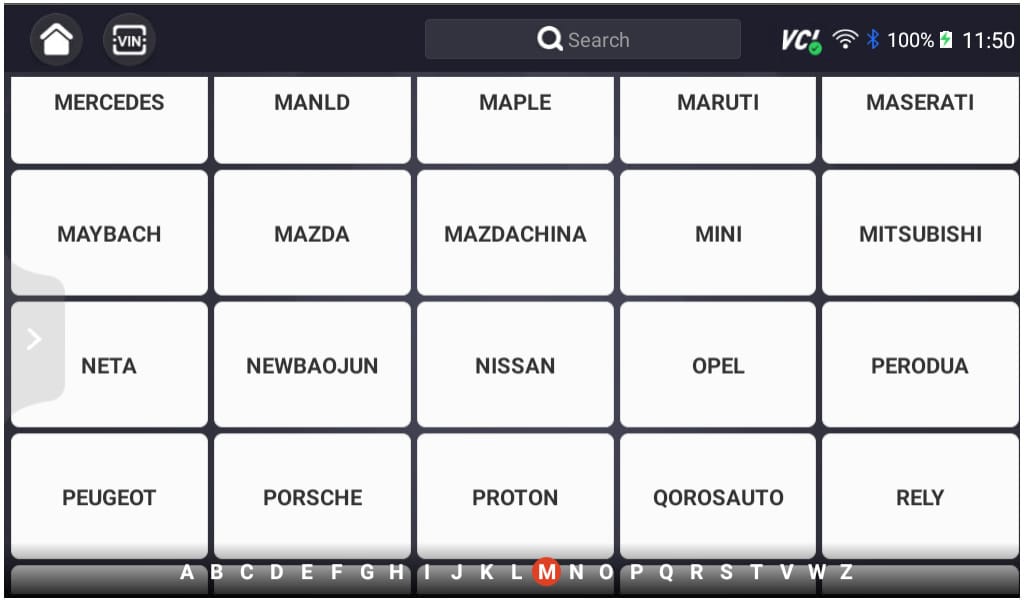
- Select ‘MITSUBISHI’ as the Vehicle Make. This ensures the scanner communicates effectively with the Mitsubishi On-Board Diagnostic system and scans fault codes effectively.

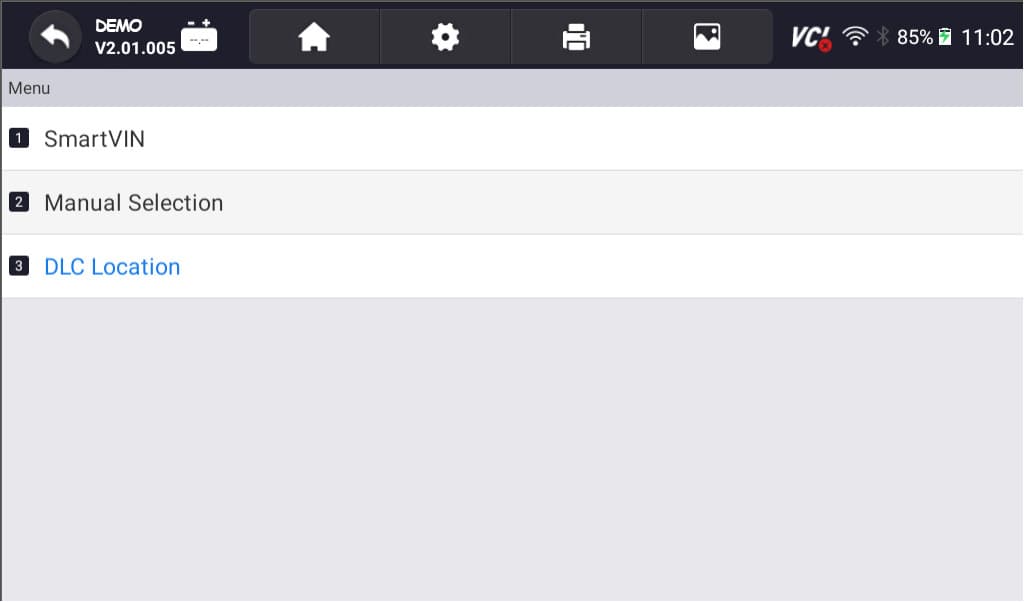
- Select option for model selection: The scanner has various options for model selection. You can choose SmartVIN to detect your vehicle automatically. However, you choose Manual Selection if SmartVIN does not work as intended.

- Select the Specific Model and Chassis: After selecting the vehicle make, scroll through the available models and select the correct one for your Mitsubishi. Choose the corresponding chassis or body type to properly sync the scanner to your vehicle.

- Select Control Units: Once you have selected the model and chassis, the scanner will let you choose between “Quick Scan” or “Control Modules.” Control Modules display a list of control units or modules in your vehicle. Examples include the engine control module (ECM), transmission control module (TCM), and ABS control module. Choose the specific module you want to diagnose. Otherwise, you can also choose the “Quick Scan” to check everything.

- Interpret the Codes: Once the YOUCANIC scanner completes the code retrieval process, the displayed codes will provide information about specific issues detected by the control unit. Take note of these codes for further analysis and diagnosis. Each DTC consists of a letter and four numbers. The letter indicates the system affected, while the numbers describe the issue more specifically. Click here to learn more about Fault codes

- Erase Codes: After the problem has been repaired, return to the scanner’s menu and select the option to “Erase Codes” or “Clear Codes.” This action removes the stored fault codes from the control unit’s memory, indicating that the problem has been resolved. Please note that you may or may not erase a code when the issue is not fixed.

NOTE: These pictures are just the demo of our YOUCANIC Scanner, it may or may not be exactly the same but the procedure is the same.
How to Decipher DTCs/Fault Codes?
DTCs are standardized codes that follow a specific format, making interpretation easier. This can be seen in the OBD scanner. Each code consists of five characters:
- The first character indicates whether the code is an SAE generic code (applies to all OBDII systems) or is specific to the vehicle manufacturer
- The second character identifies the general type of fault. For instance, ‘0’ indicates a fuel and air metering system issue.
- The third character further narrows down the fault type. It could suggest a circuit malfunction.
- The fourth and fifth characters provide a specific description of the problem.

Why Can’t I Clear My Car’s Fault Codes? Unraveling the Mystery
Once you’ve identified the DTCs, you may be tempted to clear them, hoping to continue driving your Mitsubishi, and the problem magically disappears. Clearing the codes can temporarily remove the “Check Engine” light, but it doesn’t address the underlying issue. It will always come back. Here are also some lists of why you cannot clear the codes of your Mitsubishi:
- Use a Professional-Grade Scanner: Ditch the generic scanner and upgrade to a professional-grade one like the YOUCANIC scanner. Generic scanners are like trying to open a Ferrari with a Ford key – it won’t work! YOUCANIC, on the other hand, is like the master key to your Mitsubishi’s diagnostics, unlocking hidden diagnostic powers and letting you clear codes that would otherwise remain stubborn and hidden.
- Underlying Issues: Before clearing fault codes, remember to address the underlying issue that triggered them in the first place. Clearing codes is like patching a leaky pipe without fixing the cracked valve – it’s just a temporary fix. The ‘check engine’ light will surely come back and haunt you.
- Continuous Fault Monitoring: Like the SRS system, certain fault codes may be cleared by disconnecting the battery (like a reset). They will reappear even after clearing until the root cause is resolved. It is a persistent reminder to fix the problem, not just mask it.
- Proper Clearing Procedure: Following the correct steps outlined in your diagnostic scanner’s user manual is essential to clear fault codes effectively. If unsure about the clearing procedure, consult a professional for guidance specific to your scanner and Chrysler model.
What do Live data and Freeze data mean?
Live data allows you to monitor real-time sensor readings, providing valuable insights into the car’s operation. On the other hand, Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of vehicle conditions when a fault code is triggered. Analyzing this data provides context and aids in pinpointing the root cause of the issue.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if I ignore DTCs?
Ignoring DTCs can lead to more serious problems and potentially damage your Mitsubishi’s engine or other components.
Can I clear DTCs myself?
While it’s possible to clear DTCs yourself using a basic scanner, having a professional mechanic diagnose the underlying issue before clearing the codes is recommended.
How often should I scan my Mitsubishi for DTCs?
Regularly scanning your Mitsubishi for DTCs, especially if you notice any changes in performance or feel any unusual vibrations, can help identify potential problems early on.
References
- What Is an OBD2 Scanner and How Does It Work?
What Is an OBD2 Scanner and How Does It Work? | The Drive - DTC Fault Codes
DTC Fault Codes – YOUCANIC - What Does the Check Engine Light Look Like, and What Does It Mean?
What Does the Check Engine Light Look Like, and Really Mean? – Consumer Reports - A Guide to Understanding DTC Codes
A Guide to Understanding DTC Codes (samsara.com)