Smart Car Diagnostic Trouble Codes: A Guide to Reading and Clearing with an OBD-II Scanner
In today’s high-tech automotive world, understanding and diagnosing issues in your Smart car, including popular models like Forfour, Fortwo, Cabrio Tailor Made, EQ Forfour, and others, demands advanced tools. Enter the OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanner, an essential device for car owners and enthusiasts. This professional-grade scanner is crucial, especially for luxury vehicles, offering a window into your vehicle’s health.
The OBD-II scanner serves as a bridge, decoding the complex Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) emitted by your car’s computer system. Typically displayed as a five-digit alphanumeric sequence, these codes pinpoint potential issues within your vehicle’s subsystems. Understanding these codes is key to effective vehicle maintenance and troubleshooting.
Whether you’re dealing with engine performance, emission controls, or other vehicle systems, the OBD-II scanner provides real-time diagnostic insights. Plugging the scanner into your Smart car’s diagnostic port gives you access to a wealth of data. This includes reading and, importantly, erasing fault codes that may have triggered your check engine light or other warning indicators.
Learning more about these fault codes is crucial for Smart car owners looking to maintain their vehicle’s peak performance and troubleshoot issues efficiently. Click here to deepen your understanding of OBD-II scanners and fault codes, ensuring your Smart car continues to deliver the exceptional performance you expect.
How to Read and Clear Codes on a Smart Car
- Gather the necessary tools: Equip yourself with a Professional-Grade OBD-II Scanner that is compatible with your Smart. Click Here for our Professional-Grade YOUCANIC Scanner.

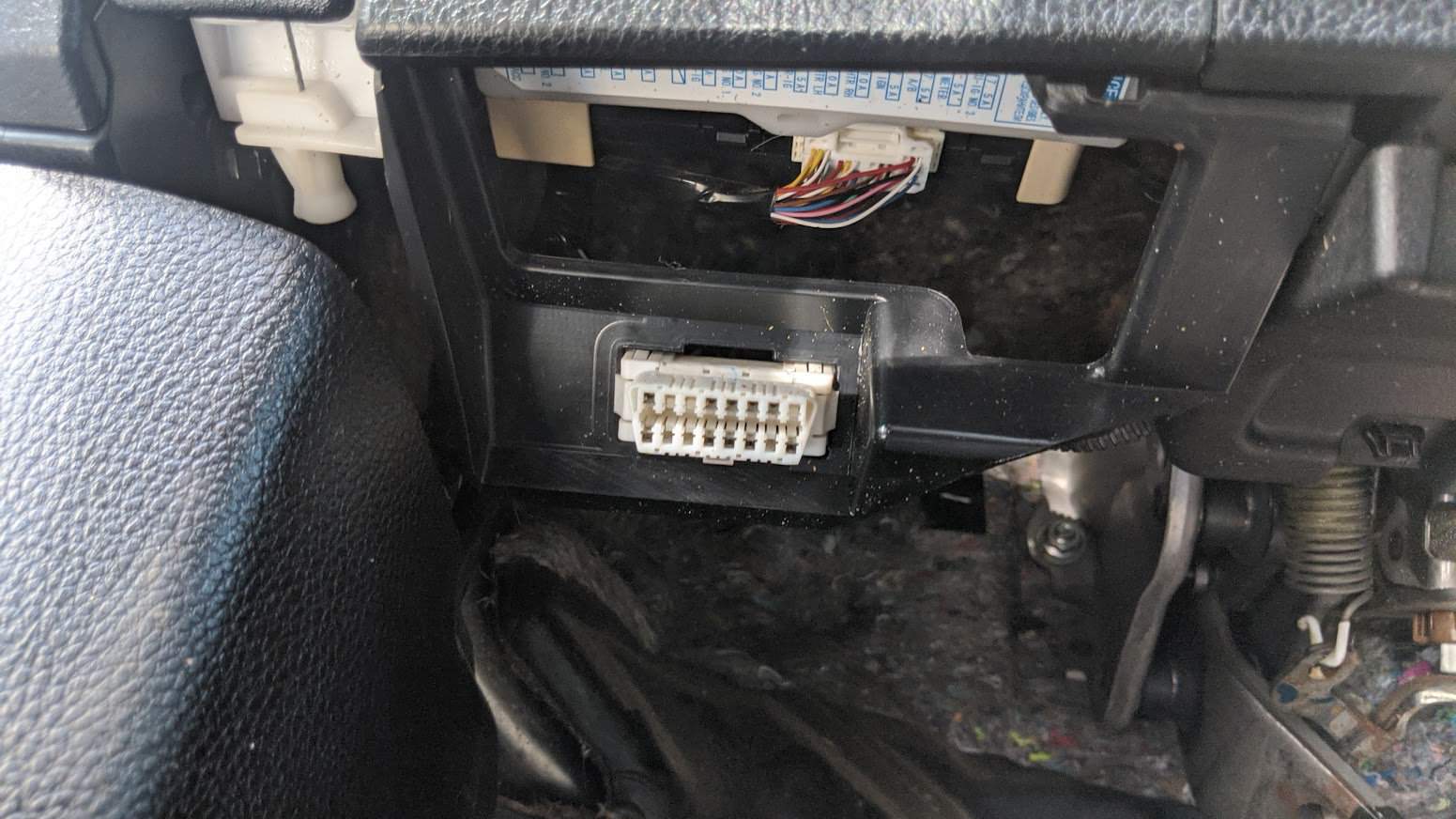
- Access the OBD-II Port: This port is usually found under the dashboard, near the steering column; the OBD-II port is the gateway to your car’s diagnostic information. Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine to make a connection with the vehicle’s computer. If your Smart has a START/STOP feature, press the button without pressing the brake pedal. Do not start the engine. If you are unsure of the OBD-II port of your vehicle, you can always check the Car Owner’s Manual.

- Access the Diagnostic Menu: On the YOUCANIC scanner’s display, navigate to the “Diagnostic” or “Scan” menu. This menu allows you to access various diagnostic functions for your Smart.

- Select ‘SMART’ as the Vehicle Make: This ensures the scanner effectively communicates with the Smart On-Board Diagnostic system and effectively scans the fault codes.

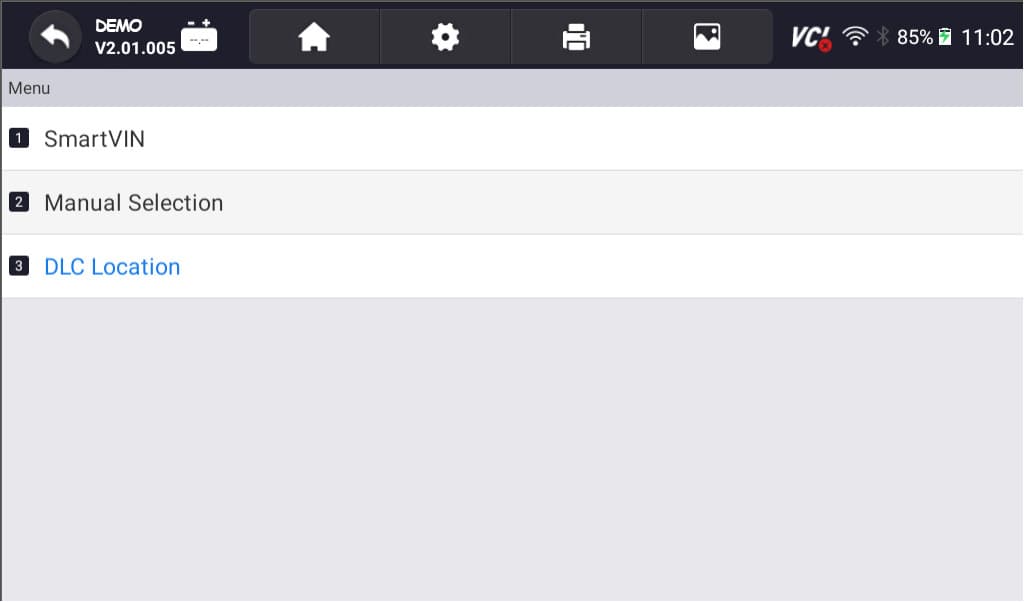
- Select option for model selection: The scanner has various options for model selection; you can choose SmartVIN to detect your vehicle automatically. However, you choose Manual Selection if SmartVIN does not work as intended.

- Select the Specific Model and Chassis: After selecting the vehicle make, scroll through the available models and select the correct one for your Smart. Choose the corresponding chassis or body type to properly sync the scanner to your vehicle.

- Select Control Units: Once you have selected the model and chassis, the scanner will let you choose between “Quick Scan” or “Control Modules.” Control Modules display a list of control units or modules in your vehicle. Examples include the engine control module (ECM), transmission control module (TCM), and ABS control module. Choose the specific module you want to diagnose. Otherwise, you can also choose the “Quick Scan” to check everything.

- Interpret the Codes: Once the YOUCANIC scanner completes the code retrieval process, the displayed codes will provide information about specific issues detected by the control unit. Take note of these codes for further analysis and diagnosis. Each DTC consists of a letter and four numbers. The letter indicates the system affected, while the numbers describe the issue more specifically. Click here to learn more about fault codes.

- Erase Codes: After the problem has been repaired, return to the scanner’s menu and select the option to “Erase Codes” or “Clear Codes.” This action removes the stored fault codes from the control unit’s memory, indicating that the problem has been resolved. Please note that you may or may not erase a code when the issue is not fixed.

NOTE: These pictures are just the demo of our YOUCANIC Scanner, it may or may not be the same but the procedure is the same.
How frequently should I scan?
Regularly scanning your Smart for DTCs is akin to giving your vehicle a check-up. It’s recommended that you scan your car at least once a year or more frequently if you notice any performance issues or warning lights illuminate.
Check our article here if you want to know what is the best OBD-II for DIY Enthusiasts: Best OBD2 Scanner For DIY Auto Repair – YOUCANIC
Is it important to scan my vehicle?
There are several reasons why you should scan your vehicle for fault codes:
- To identify the source of the problem. Fault codes can help you pinpoint the specific problem with your vehicle. This can save you time and money on repairs.
- To prevent further damage. Ignoring fault codes can lead to further damage to your vehicle and it can be dangerous as well.
- It can improve fuel efficiency, and depending on the malfunctioned part, fixing problems that are causing fault codes can also improve a vehicle’s fuel efficiency.
- To pass emission testing in some states, you may be required to have your vehicle scanned for fault code before you can pass emission testing
I can’t clear the codes after scanning them.
Once you’ve identified the DTCs, you may be tempted to clear them, hoping to continue driving your Smart, and the problem magically disappears. Clearing the codes can temporarily remove the “Check Engine” light, but it doesn’t address the underlying issue. It will always come back. Here are also some lists of why you cannot clear the codes of your Smart:
- Use a Professional-Grade Scanner: Ditch the generic scanner and upgrade to a professional-grade one like the YOUCANIC scanner. Generic scanners are like trying to open a Ferrari with a Ford key – it won’t work! YOUCANIC, on the other hand, is like the master key to your Smart’s diagnostics, unlocking hidden diagnostic powers and letting you clear codes that would otherwise remain stubborn and hidden.
- Underlying Issues: Before you go clearing fault codes, remember to address the underlying issue that triggered them in the first place. Clearing codes is like patching a leaky pipe without fixing the cracked valve – it’s just a temporary fix. The ‘check engine’ light will surely come back and haunt you.
- Continuous Fault Monitoring: Certain fault codes, like the SRS system may be cleared by disconnecting the battery (like a reset). They will reappear even after clearing until the root cause is resolved. Think of it as a persistent reminder to fix the problem, not just mask it.
- Proper Clearing Procedure: To clear fault codes effectively, follow the correct steps outlined in your diagnostic scanner’s user manual. If you are unsure about the clearing procedure, consult a professional for guidance specific to your scanner and Smart model.
What happens when I ignore the fault codes?
It can lead to some problems like further damage to your vehicle because the problem that is causing the fault code may get worse and cause further damage.
Ignoring fault codes can lead to increased emissions, which can harm the environment.
Failure to pass emission testing could happen if you ignore fault codes, you may not be able to pass the emission testing in your state.
What do History, Current, and Stored DTCs do?
- History: These codes indicate past issues that have resolved themselves or are no longer causing the “Check Engine” light to illuminate. They typically do not require immediate attention.
- Current Codes: These codes represent current or active problems that require immediate diagnosis. They indicate a present issue or malfunction in a specific system or component of the vehicle that needs to be addressed. They will remain displayed until the underlying issue is resolved.
- Stored Codes: These codes are inactive but remain stored in the computer’s memory, recording previous issues. These can provide additional information about past issues as a historical reference for previous faults. While they may not be active, they can offer insights into the vehicle’s history and aid in the diagnostic process.

Please click here if you want to know more about the history, current, and stored DTCs.
The purpose of Live Data and Freeze data?
Live data allows you to monitor real-time sensor readings, providing valuable insights into the car’s operation. On the other hand, Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of vehicle conditions when a fault code is triggered. Analyzing this data provides context and aids in pinpointing the root cause of the issue.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Can I clear DTCs myself?
Yes! While clearing DTCs can temporarily turn off the “Check Engine” light, it doesn’t address the underlying issue. It’s recommended to have a qualified mechanic diagnose and repair the problem first before you clear all the codes. You can also ask for professional assistance.
How Often should I check for DTCs?
Regularly checking for DTCs can help you identify potential issues early on, preventing more serious problems down the road. You can also use it whenever a check engine light illuminates to diagnose or check why your car is acting up.
What are the benefits of using a professional-grade scanner?
Professional-grade scanners provide more detailed information, manufacturer-specific codes, guided diagnostics, and component testing capabilities, making them valuable tools for accurate diagnosis and repair.
What are the most common Smart DTCs?
The specific DTCs vary depending on the vehicle’s model and year. However, some common ones include P0171 (system too lean), P0304 (cylinder 4 misfires detected), and P0422 (catalyst system efficiency below threshold).
References:
- The Drive – What Is an OBD2 Scanner and How Does It Work?
What Is an OBD2 Scanner and How Does It Work? | The Drive - YOUCANIC – DTC Fault Codes
DTC Fault Codes – YOUCANIC - ConsumerReports – What Does the Check Engine Light Look Like, and What Does It Mean?
What Does the Check Engine Light Look Like, and Really Mean? – Consumer Reports - YOUCANIC – Current / Stored / Active / Past / History Fault Codes Explained
Current / Stored / Active / Past / History Fault Codes Explained – YOUCANIC